Right-angled descending broadening wedge
-
- 1
- Who voted?
- 10427
- 0
What is a right-angled descending broadening wedge?
A right-angled descending broadening wedge is a bullish reversal pattern. The pattern is formed by two diverging lines, the resistance being a horizontal line and the support a bearish downward slant, so it is an inverted ascending triangle. The oscillations between the two triangle terminals are therefore becoming increasingly large. Each line must be touched at least twice to be validated.
The right-angled descending broadening wedge reflects the growing nervousness of investors and also their indecision. If the chart pattern is not spotted quickly, the movements may appear totally random and thus trap many investors.
The formation of this pattern has to be preceded by a bullish movement. Although one might think that this pattern is a reversal pattern because of its shape, it is more a sign of a weakness on the part of sellers beginning a bearish trend.
The price objective is given by plotting the top point of the triangle at its start where it breaks out. Another technique consists in plotting the maximum height of the triangle at the break out point.
Graphic representations of a right-angled descending broadening wedge
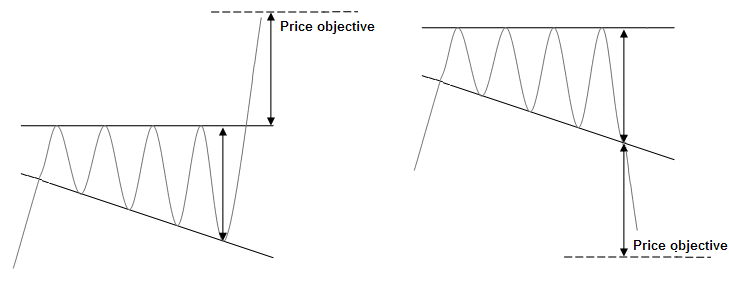
Statistics of a right-angled descending broadening wedge
Here are some statistics about a right-angled descending broadening wedge:
- In 57% of cases, there is a bullish exit
- In 90% of cases, the minimum objective of the pattern is achieved by using the technique of the maximum height of the triangle. In the event of a downward exit, the percentage drops to 70%.
- The failure rate is 6% (i.e. a horizontal exit).
- In 23% of cases, there is pullback in the case of a bullish exit and 33% in the case of a bearish exit
Comments on a right-angled descending broadening wedge
- Bullish exits perform better bearish exits
- The movement is greater in a bullish breakout
- The configurations that perform best are those that are preceded by a large movement before the triangle is formed.
- Bullish breaks occur in 75% of cases in the upper third of the annual range
- Pullbacks are detrimental to performance
Trading strategies with right-angled descending broadening wedges
The traditional strategy:
Entry: Opening a long position at the resistance break
Stop loss: The stop loss is placed below the resistance
Objective: Theoretical objective of the pattern
Advantage: Minimum objective very often achieved (90% of cases) and pullbacks are infrequent
The aggressive strategy:
Entry: Opening a long position on the 3rd contact with the support line
Stop loss: The stop loss is placed below the last lowest point
Objective: Opposite boundary of the triangle then possibly theoretical objective of the pattern
Advantage: The amplitude of the movement will be significant in the event of a bounce towards the opposite terminal. Low risk
Disadvantage: Bearish exits in 37% of cases
For your information: The pattern in a right-angled descending broadening wedge is a reversal pattern. Its opposite is the pattern in a Right-angled ascending broadening wedge.
About author
- 20
- 42
- 61
- 6





